
briefAs the G2E (Global Gaming Expo) conference kicks off in Las Vegas, it's vital to emphasize the important role that cybersecurity plays in the rapidly evolving gaming industry. From online casinos to eSports, the gaming industry has grown into a massive global enterprise that has become a prime target for cybercriminals. With attacks ranging from DDoS outages to account takeovers, the industry's digital infrastructure is under constant threat. This blog will look at the latest cyber threats affecting the gaming industry, the tactics used by attackers and the steps developers and operators can take to protect their platforms.
The Rise of Cyber Threats in the Gaming Industry
The gaming industry has experienced exponential growth over the past decade, emerging as a dominant force in the global entertainment market. Once a niche hobby, gaming has evolved into a multi-billion dollar industry that generates more revenue than the movie and music industries combined. According to recent reports, driven by the rise of mobile gaming, eSports, and the expansion of online multiplayer gaming platforms, the size of the global gaming market is expected toOver $300 billion by 2026. The explosion of the game has attracted billions of users worldwide, creating a large and interconnected network of players. However, this growth has also raised unwanted concerns. With such a large user base and huge financial benefits, the gaming industry is an attractive target for cybercriminals looking to exploit its size, infrastructure and vulnerabilities.
The gaming industry has a unique combination of factors that make it particularly vulnerable to cyberattacks. One of the primary reasons for this is the vast amount of personal data collected from users, including personally identifiable information such as names, email addresses, credit card information, and even IP addresses. Many games also include in-game currency or valuable digital items, which are often targeted by attackers seeking quick financial gain. Additionally, the prevalence of younger gamers, who may be less cautious about cybersecurity, provides the perfect opportunity for phishing schemes and social engineering attacks. These users are often more focused on gaming than protecting their accounts, leaving them vulnerable to password theft, account takeovers and other malicious activity. The rise of microtransactions, the digital economy, and competitive gaming further enhances the appeal to cybercriminals who see the gaming ecosystem as a lucrative target for fraud, data theft, and financial exploitation.
Common Cyber Threats in the Gaming Industry
As the gaming industry continues to expand, it faces cyber threats from multiple sources. Players and developers alike are becoming increasingly vulnerable to attacks that can disrupt gameplay, compromise sensitive information and undermine trust in the platform. Here are some of the most common types of attacks targeting the gaming industry.
DDoS attack: Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks have become a frequent and disruptive problem in the gaming industry. These attacks overwhelm servers with massive amounts of traffic and are often used to disrupt multiplayer gaming platforms, interrupt matches, or disrupt the online gaming experience for millions of players.DDoS attacks are often launched by disgruntled gamers or cybercriminals to extort ransom from game developers and companies in exchange for stopping the attacks. In competitive gaming, even a brief outage can lead to significant financial losses and frustration among the user base. The frequency of these attacks is so high that gaming companies must invest in robust DDoS mitigation strategies to ensure uninterrupted gaming and protect their services.
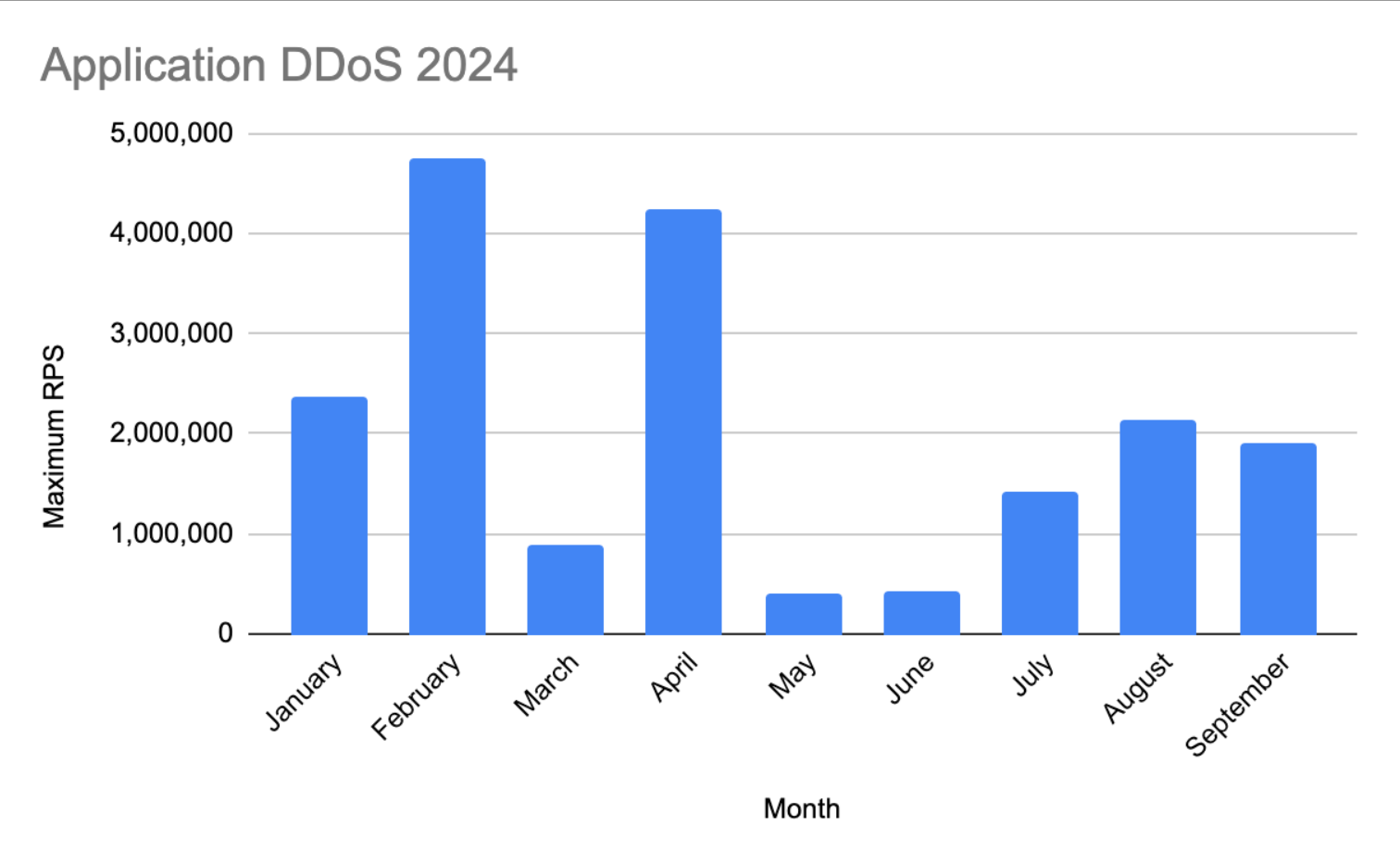
In the first half of 2024, gaming sites were hit by thousands of DDoS attacks. One of the largest application layer (L7) DDoS attacks at the time saw a gaming site in Indonesia hit with nearly 5 million requests per second (RPS) in just 13 minutes.
Earlier this year, the gaming industry suffered several large-scale attacks, and the number of attacks has begun to increase since the summer. As the holidays approach, we can expect the number of attacks to increase as companies announce holiday releases and increased demand.
Phishing, social engineering and account takeover: Phishing scams and social engineering tactics are among the most common threats to gamers and developers. Cybercriminals can pose as official game developers or support teams and trick players into providing sensitive information such as login credentials, credit card details or access to in-game assets. In many cases, attackers use fake login portals or email campaigns to trick users into providing passwords or personal information, which is then used to steal accounts or sold on the black market. This year alone, information-stealing malware targeting gamers collectedmillionsStolen credentials from Discord, Battlenet, Activision, UnknownCheats and other online gaming centers.
Game developers are not immune to these tactics, as phishing attempts can target their credentials to gain unauthorized access to internal systems or development platforms. These attacks can result in the theft of proprietary data, unpublished game content, or intellectual property, which can cause significant damage to players and companies.
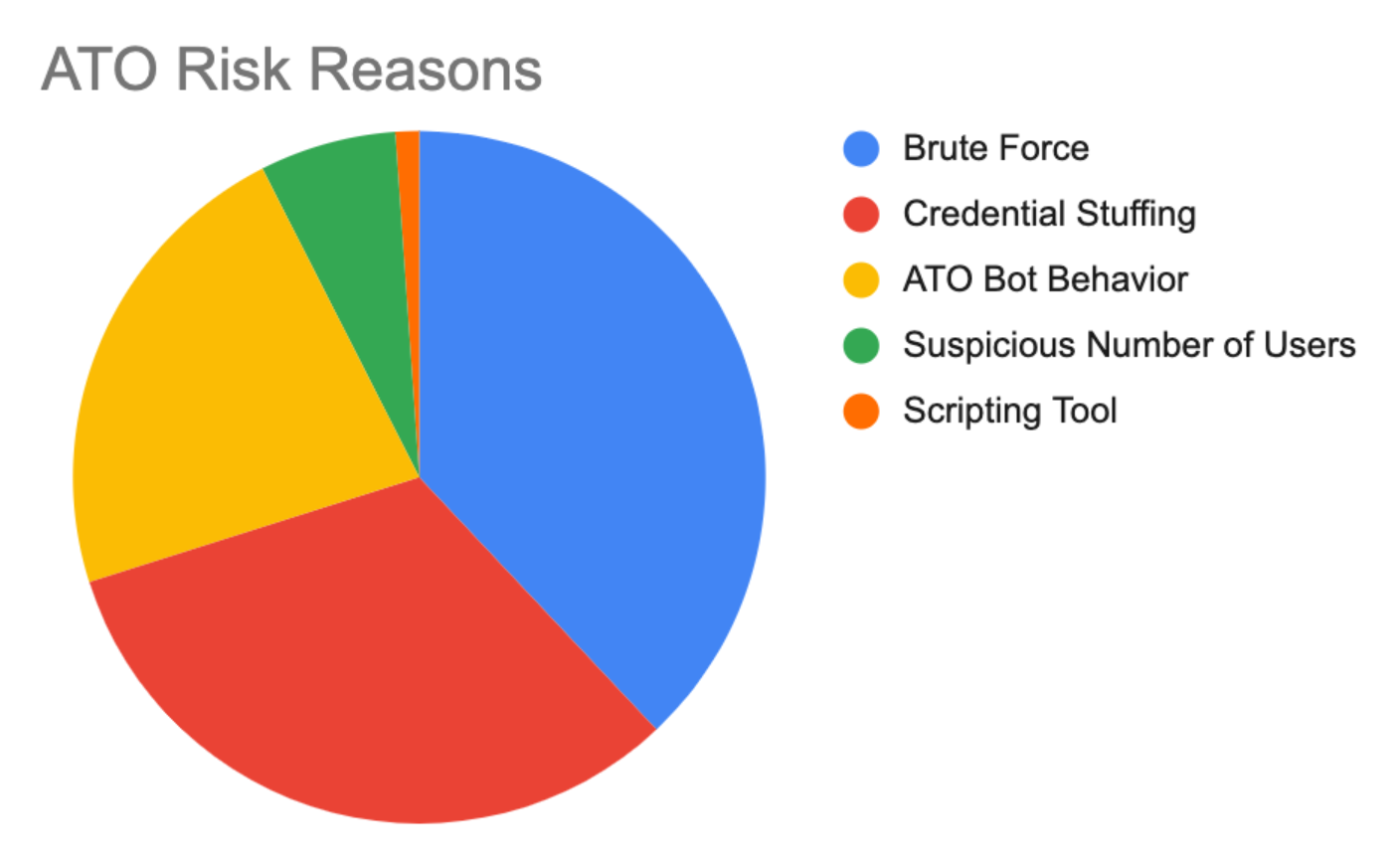
Account Takeover Attacks (ATOs) have also become a major problem for the gaming industry, as stolen game accounts often contain valuable in-game items, digital currency and personal information. Cybercriminals often use brute-force attacks, credential stuffing or phishing tactics to compromise player accounts, which are then sold on the black market or used for fraudulent activities. The black market for gaming accounts is lucrative, especially for games with rare items or premium characters. Once an account is stolen, recovering it can be a difficult and time-consuming process, with players often losing digital assets and personal data. For developers, widespread account takeovers can lead to loss of trust, decreased player engagement and negative publicity.
On average, the gaming industry suffers an average of nearly 9,000 account takeover attacks per day. Of these attacks, brute force and credential stuffing account for nearly 75% of the total causes of risk. unsurprisingly, bots are the most popular tool for conducting these attacks, although browsers come in second.
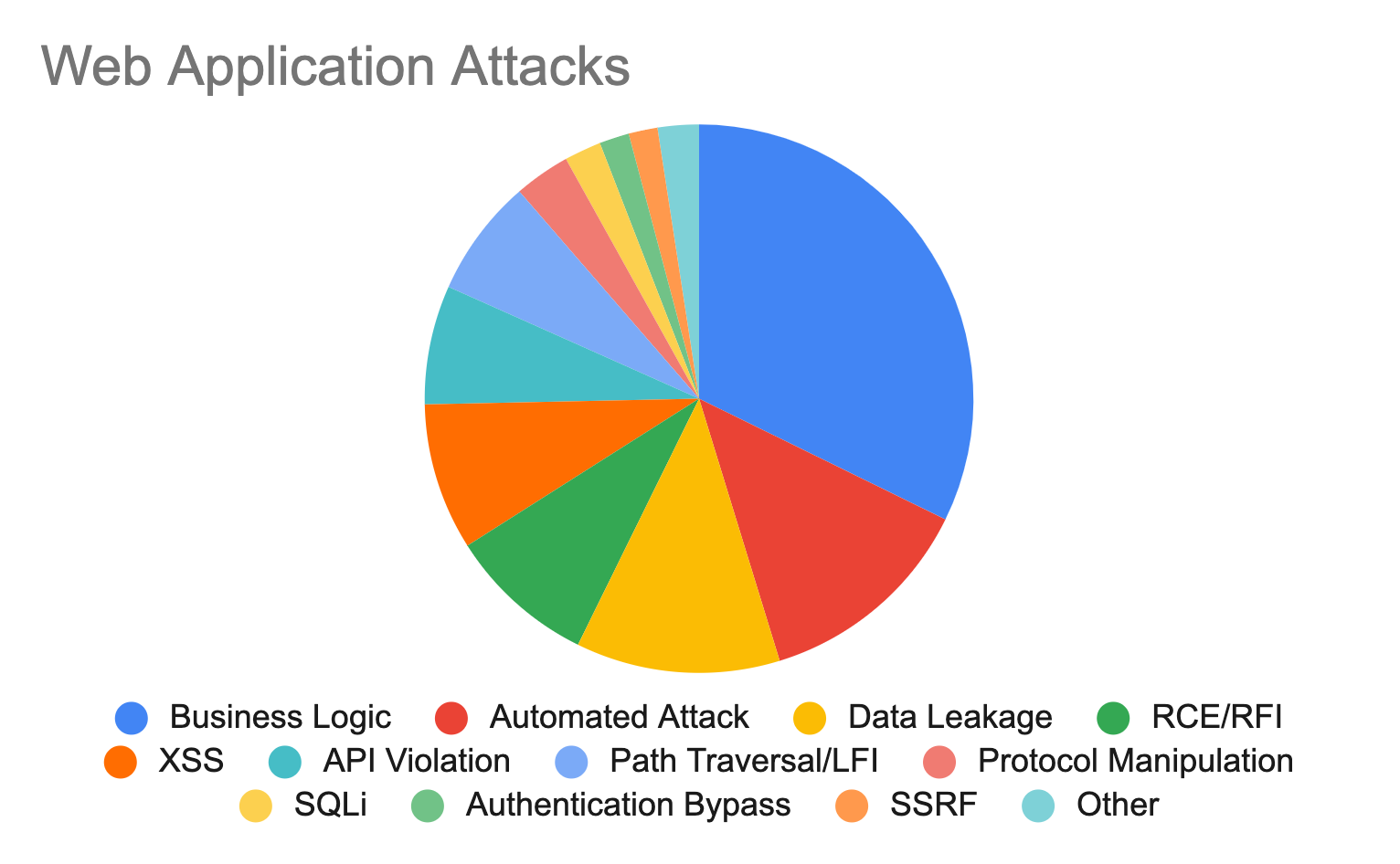
Web application attacks:Gaming platforms are often subject to a variety of attacks against web applications. These attacks typically attempt to exploit vulnerabilities in application code or APIs to gain unauthorized access or compromise systems. Approximately 7% of Web attacks targeted API endpoints, which highlights the critical role that APIs play in cybersecurity, as even a small portion can lead to serious vulnerabilities.
Remote Code Execution (RCE) attacks allow hackers to execute arbitrary commands on a server, potentially compromising sensitive data and disrupting game functionality. Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities allow attackers to inject malicious scripts into web pages, which can lead to data theft and user impersonation. API violations occur when an attacker exploits weaknesses in the APIs used to integrate various game features, which can lead to unauthorized access or manipulation of game data. Business logic attacks exploit flaws in application workflows that enable cheating or unauthorized manipulation, which can compromise the integrity of the game. Combined, these attacks can have a serious impact on game security, player experience, and overall trust in online gaming platforms.
The Impact of Cyber Attacks on the Gaming Industry
Cyberattacks in the gaming industry can have far-reaching consequences - reputational, legal and financial - for game developers and players. For developers, direct costs can include lost revenue due to downtime caused by DDoS attacks, ransom payments following a ransomware incident, or the financial strain of recovering from a data breach. Long-term disruptions to gaming platforms can result in millions of dollars in lost transactions, especially for games that rely on real-time purchases or subscriptions. For players, the theft of in-game assets, digital currency, or personal payment information can result in significant financial losses, especially for games in which users have invested heavily in virtual goods. In addition to these direct costs, companies must also consider the costs of repairing compromised systems, enhancing security, and compensating affected users.
Reputational damage from cyberattacks is often as bad as the financial losses.2021, game developersCD Projekt RedA ransomware attack that led to a leak of source code and delays in the development of its game Cyberpunk 2077, which has already been criticized for exploits and player issues, has further fueled distrust in the company. When a gaming company suffers a security breach, it can lose the trust of its players, which is crucial to maintaining a strong, loyal user base. Players who feel their data is insecure are more likely to stop playing the game or avoid future purchases, leading to a drop in user engagement and revenue. Negative media coverage and social media outcry can further damage a gaming company's reputation, deterring new users from joining and prompting existing players to seek safer alternatives. Reputational damage can last long after the initial attack and can be difficult to fully recover from, even if a company increases its security measures.
The legal and regulatory consequences of a cyberattack on the gaming industry can be severe, especially for companies that fail to protect their users' personal data. With increasing scrutiny of data privacy and security globally, many countries have implemented strict regulations, such as Europe'sGeneral Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)The U.S.California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)and for credit card informationPCI DSS 4.0.. Violations of these regulations can result in significant fines, lawsuits, and class action lawsuits filed by affected players. In addition to financial penalties, companies may be required to implement costly compliance measures, undergo audits and publicly disclose violations, further damaging their reputation. For gaming companies, ensuring strong security practices isn't just a matter of protecting users; it's also critical to complying with evolving legal standards.
Protecting the Gaming Industry from Cyber Threats
As cyberattacks against the gaming industry continue to grow in size and sophistication, a comprehensive approach to security is critical. For developers, implementing strong security measures is key - protecting sensitive data with encryption, securing user accounts with multi-factor authentication (MFA), and conducting regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities. Commercial security solutions such as Web Application Firewalls (WAFs), DDoS protection services, data security solutions and advanced threat detection tools can also bolster defenses. On the player side, it is important to be aware of security best practices, such as recognizing phishing attempts, using strong passwords, and maintaining security awareness when interacting with other players or installing modifications. Players should activate MFA and only install games from trusted sources.
Best Practices:
- Use end-to-end for sensitive dataencrypted.
- Require multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all user accounts and administrative logins and promote the use of strong passwords.
- utilizationRobot Management Solutionsto prevent account takeovers and unnecessary consumption of site resources.
- utilizationAPI Securitysolutions to protect endpoints.
- Perform periodic security audits to identify potential vulnerabilities.
- investorsDDoS Protectionservices to mitigate large-scale attacks designed to disrupt gameplay.
- deploymentsWeb Application Firewall (WAF)to defend against common Web-based attacks, including SQL injection and cross-site scripting.
- Raise awareness of phishing scams and social engineering tactics and advise players to avoid suspicious links.
- Ensure that gamers only download games or patches from official, trusted sources and are advised to use anti-virus solutions and be careful when installing untrusted game modifications.
reach a verdict
As the gaming industry moves into new areas of digital entertainment and online gaming, the threat landscape continues to expand. Cyber-attacks can lead to financial losses, data breaches and reputational damage, but these risks can be minimized by taking proactive security measures. As we gather at G2E to celebrate gaming innovation, it's a reminder to prioritize cybersecurity and protect this dynamic industry from evolving cyber threats.